![]()
 Full name: Republic of Zambia
Full name: Republic of Zambia
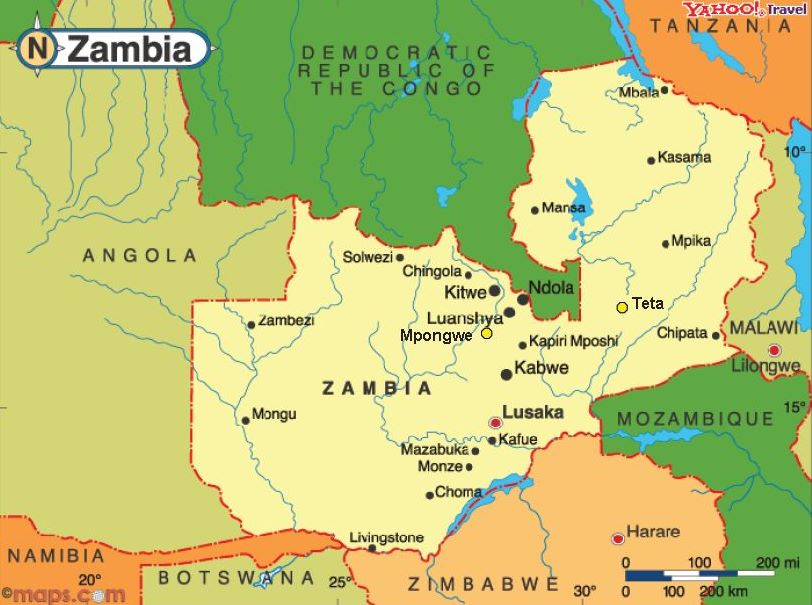
 Location: Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, surrounded by Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, Tanzania och Mozambique.
Location: Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, surrounded by Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, Tanzania och Mozambique.
Capital: Lusaka Main cities: Ndola, Kitwe, Chipata, Kabwe, Livingstone.
Size: slightly larger than Texas, 1½ times as large as Sweden
Climate: tropical; rainy season (October to April), periodic drought
Major language: English (official), Bemba, Lozi, Nyanja, Tonga. The language used in Mpongwe district is Lamba.
Religion: Christian Over 90%, Small Muslim and Hindu minority, indigenous belief. A strong presence of Jehovah’s Witnesses.
Electricity: 23% of people have access to electricity in their homes. (2003)
 National Wealth: Zambia has spectacular scenery, including the Victoria Falls along the Zambezi river, the Bangweulu Swamps and the Luangwa river valley. There is an appealing music and dance tradition.
National Wealth: Zambia has spectacular scenery, including the Victoria Falls along the Zambezi river, the Bangweulu Swamps and the Luangwa river valley. There is an appealing music and dance tradition.
Wildlife: Zambia has abundant wildlife with several of the worlds best game reserves, one of which is near Mpongwe.
Early missionaries at Mpongwe Mission gave care to a man who had been attacked by a leopard but wild game has been gone from the Mpongwe area since the 1930’s, although the hospital has treated crocodile bites in more recent years.

Population: 11.86 – 12.2 million* Zambia hosts tens of thousands of refugees who have fled conflicts in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Angola and Zimbabwe. The population of Mpongwe District population stands at 80,456 with a birth rate of 5.8 per cent.
*The lower population estimate takes into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; resulting in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (CIA estimate July 2009 est.). The higher number is the UN, 2008 official number)
ECONOMY
Monetary unit: 1 Kwacha = 100 ngwee. 1 USD is about 5000 Zambian Kwacha.
Main exports: Copper, minerals, tobacco
Gross national income (GNI) per capita: US $800 (2007)
GDP per capita (PPP): $1,500 (2008 est.)
GDP real growth rate: 5.8% (2008 est.)
Unemployment rate: 50% (2000 est.)
Aid from all countries: US$945 million (2005), Aid as proportion of GDP is 13%
Zambia moved from being a major copper producer and potentially one of Africa’s richest countries at independence in 1964 to one of the world’s poorest. A colonial legacy, mismanagement, debt and disease have contributed to the country’s problems. Privatization of government-owned copper mines in the 1990s relieved the government from covering mammoth losses generated by the industry and greatly improved the chances for copper mining to return to profitability and spur economic growth. Copper output has increased steadily since 2004, due to higher copper prices and foreign investment. The late president, Levy Mwanawasa, won respect for his anti-corruption drive. In 2005, Zambia qualified for debt relief under the Highly Indebted Poor Country Initiative, consisting of approximately USD 6 billion in debt relief. AIDS is blamed for decimating the cream of Zambian professionals – including engineers and politicians – and malaria is a major problem.
Zambia’s economy has experienced modest growth in recent years, with real GDP growth in 2005-07 between 5-6% per year. Improved copper prices and investment in mining have improved prospects for export earnings. Zambia experienced a bumper harvest in 2007, which helped to boost GDP and agricultural exports and contain inflation. Although poverty continues to be significant problem in Zambia, its economy has strengthened, featuring single-digit inflation, a relatively stable currency, decreasing interest rates, and increasing levels of trade. The decline in world commodity prices and demand will hurt GDP growth in 2009
Facts compiled from
CIA The World Factbook, UN Human Development Report 2008, BBC Fact Page, Unicef and SIDA . Updated April 2009